Insulation
Insulation Guide
What to insulate?
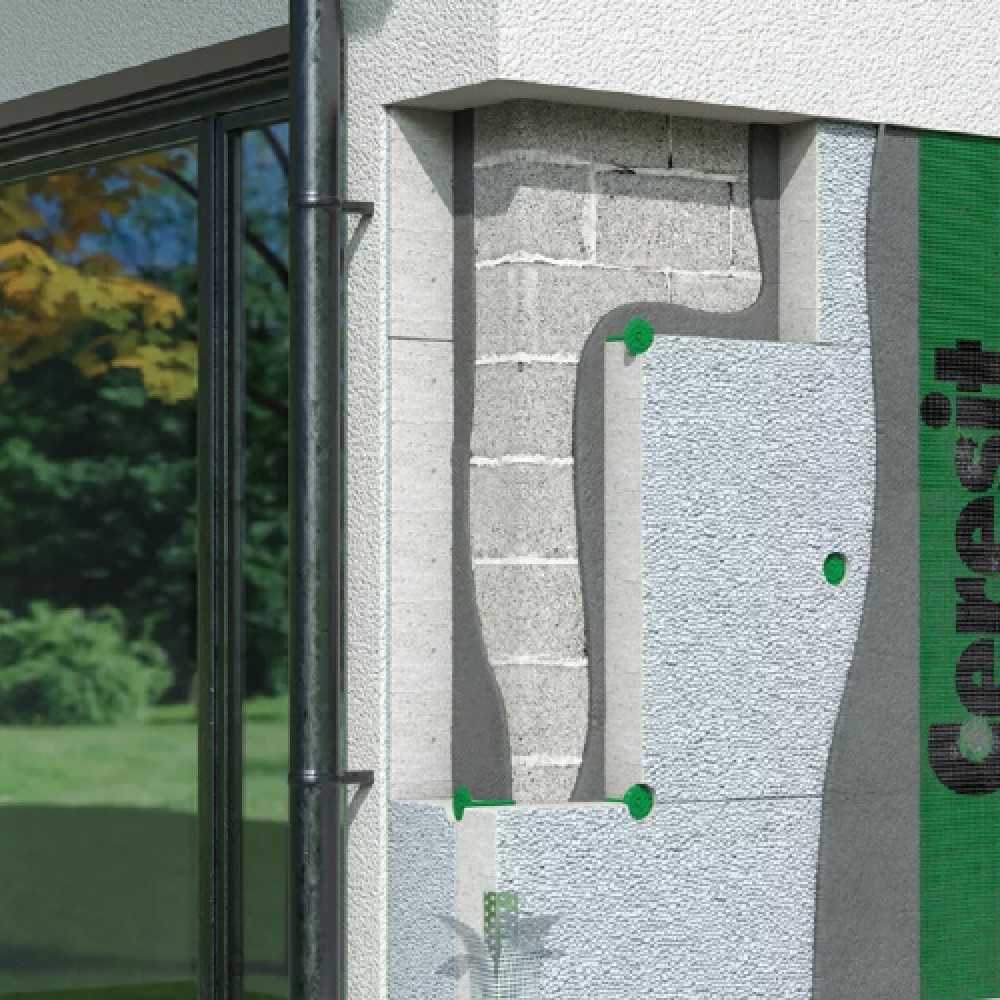
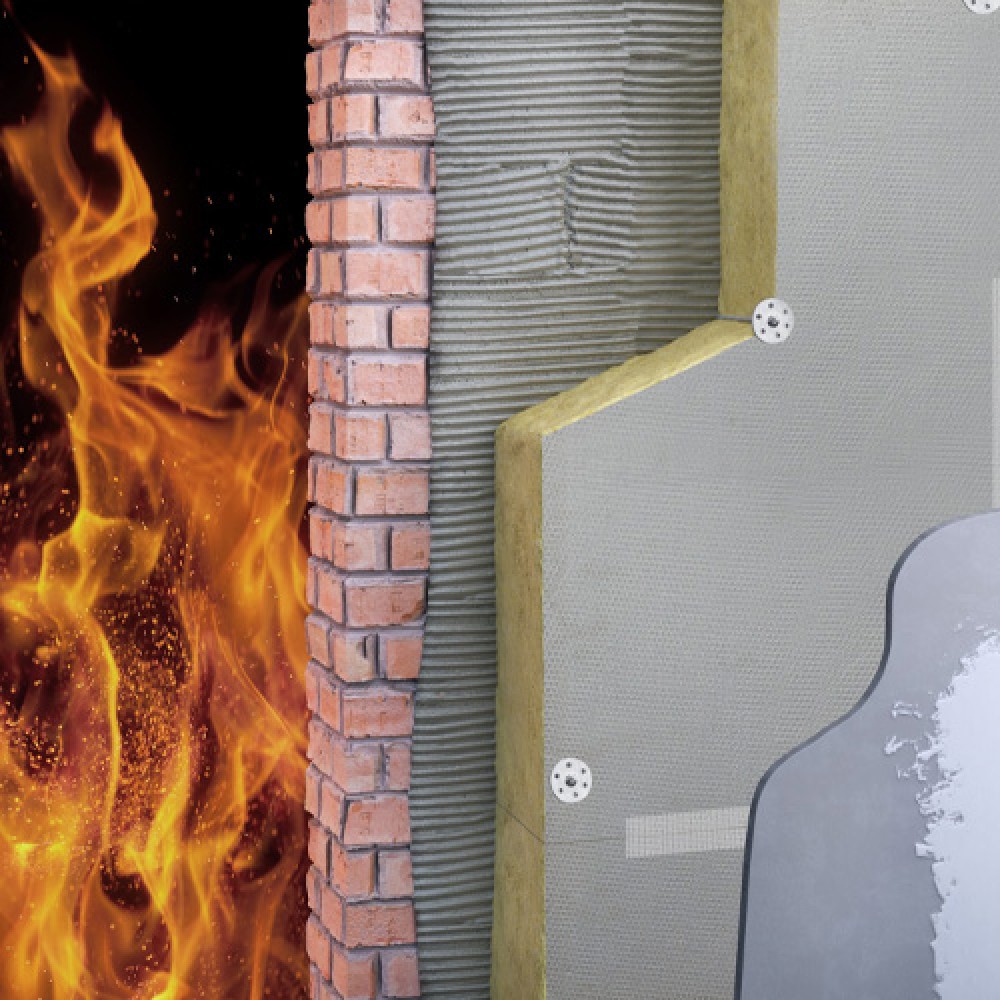
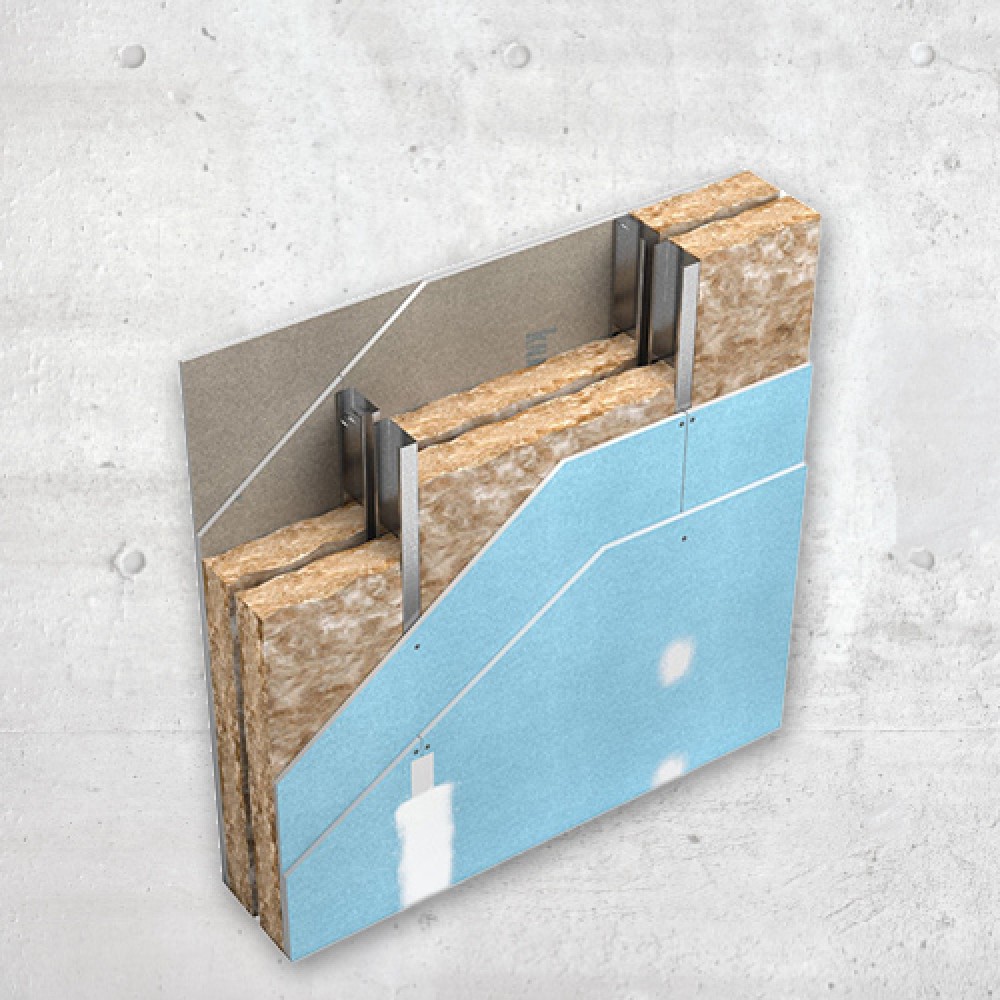
cavity wall insulation
Cavity wall insulation is used to reduce heat loss through a cavity wall by filling the air space with a porous material.
During construction of new buildings, cavities are often filled with fibre glass wool, rock wool slabs (batts) or rigid PIR insulation boards placed between the two sides of the wall.
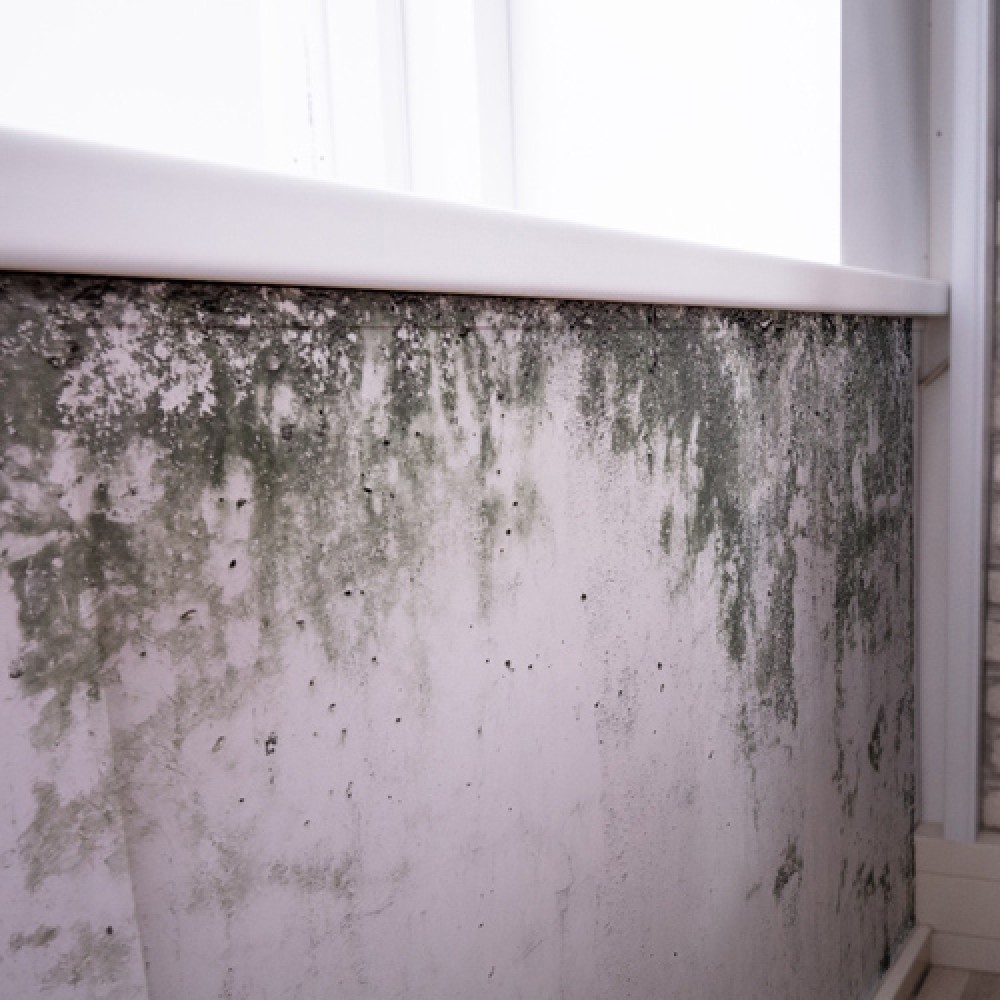
For existing buildings that were not built with insulated cavities, a fibrous material such as cellulose insulation or glass wool is blown into the cavity through suitably drilled holes until it fills the entire wall space. Foam can also be used for this purpose. Cavity wall insulation is an effective way to save energy and money it can give you an annual saving of around £115* So, insulating your cavity walls will help you to heat your home more efficiently. Using less energy reduces carbon dioxide emissions (CO2): one of the biggest causes of climate change. Cavity wall insulation can also help to reduce condensation inside the house.
buy cavity insulation
solid wall insulation
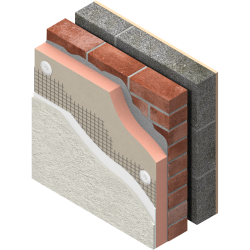
Solid brick, solid stone, timber frame (pre 1944) and concrete constructed houses can all improve their thermal efficiency by either lining the interior of the external walls with a insulating material like: rigid insulation boards( polyfoam, PIR polystyrene, phenolic), insulation slabs or by rendering the outside walls with a protective insulating layer (polystyrene, polyfoam, phenolic).
What is a solid wall?
- 9” masonry walls and other non-traditional construction types such as single leaf masonry, >9” walls (e.g. thick stone walls)
- Concrete walls, metal or timber panels and some mixed wall types (e.g. Where the ground and first floors are constructed of different materials)
- BRE estimate that around 7% of unfilled cavity wall stock cannot receive CWI.
- High rise flats (at least 6 storeys high) – esp. 1953-1972
Solid wall insulation is an effective way to save energy and money it can give you an annual saving of around £365-385*. It can make your home warm and cosy and can help with condensation problem.
buy wall insulation
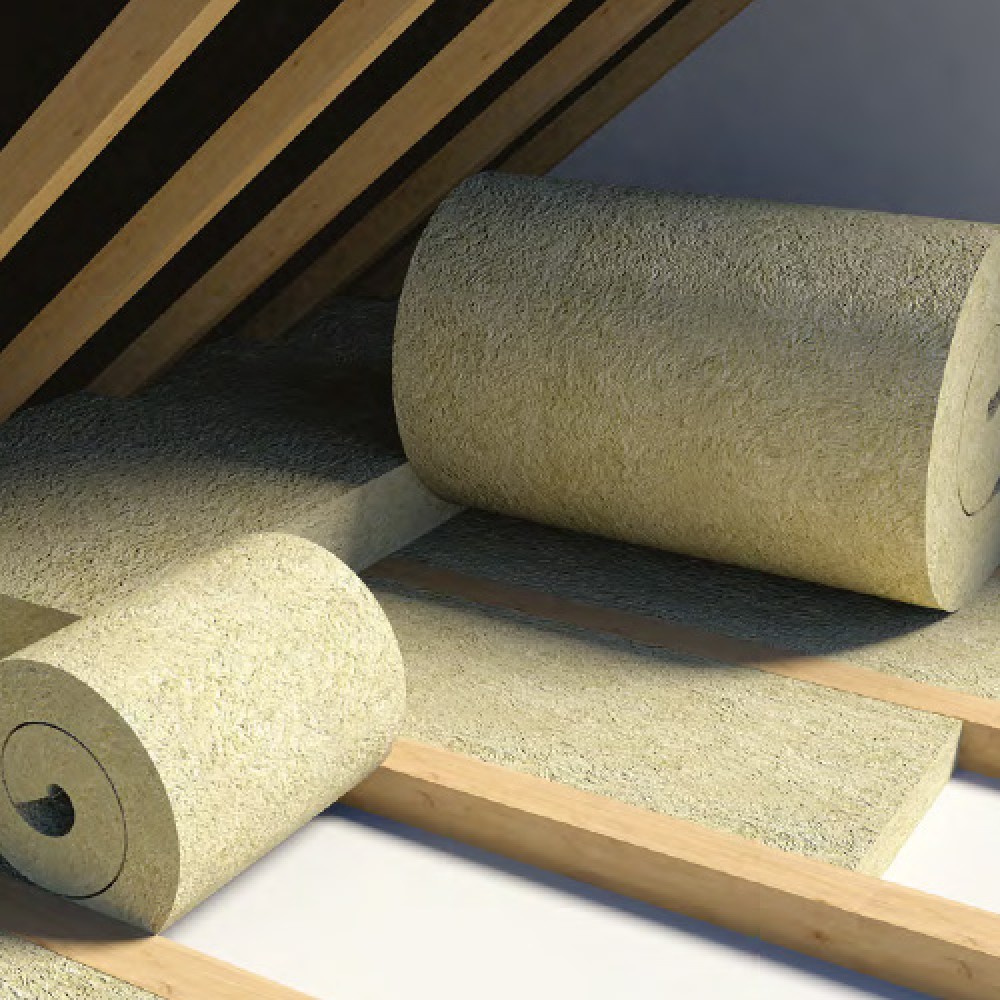
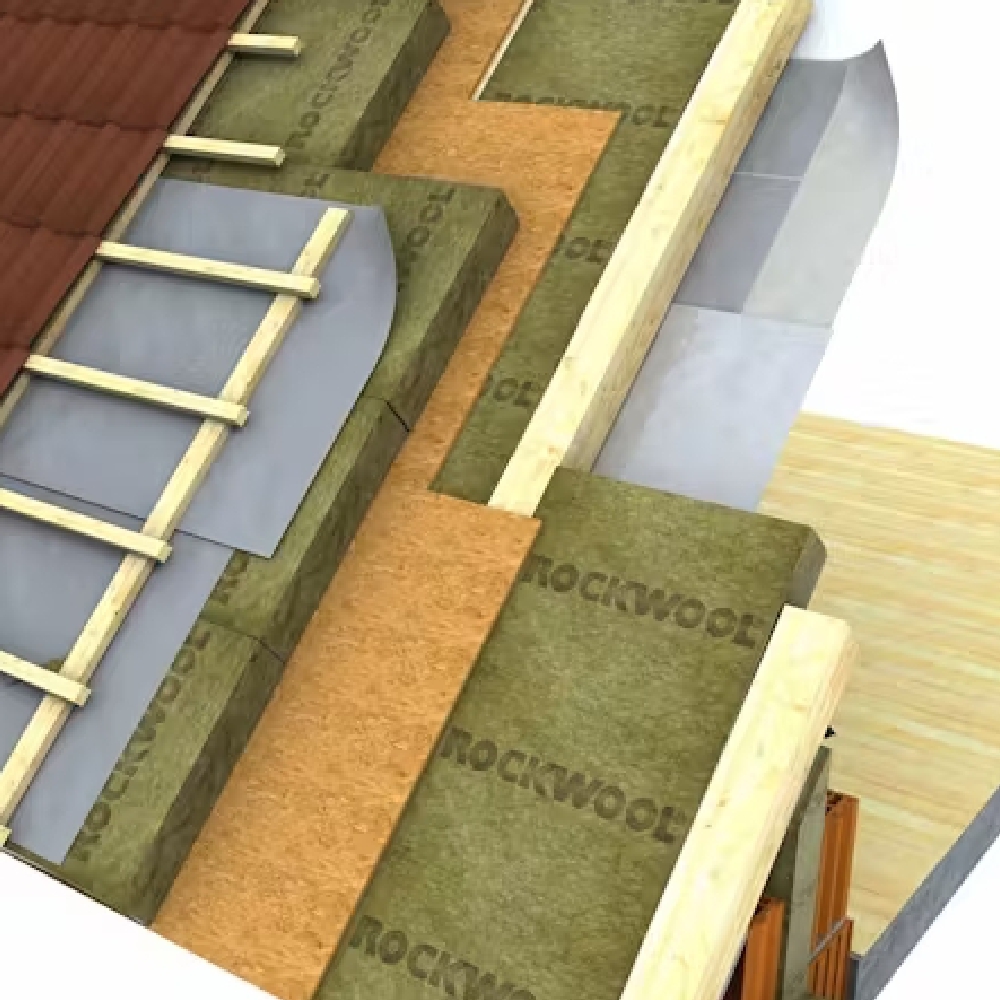
loft insulation
Loft insulation is located between the joists on the loft floor of a property.
Home is a perfect candidate for loft insulation if it has an accessible loft with no damp or condensation problems.
For lofts with difficult access, blown insulation can be used however this must be installed by an installer
The main materials used for loft insulation are Mineral Wool (Glass or Rock Wool),
The recommended depth for loft insulation is 270 millimetres for glass wool, 250 millimetres for rock wool or 220 millimetres for cellulose.
Loft Insulation can help lower your heating bills, giving you an annual saving between £45 to £150 .
It can also lower wear and tear on your boiler and reduce global warming and climate change
Buy loft and ceiling insulation
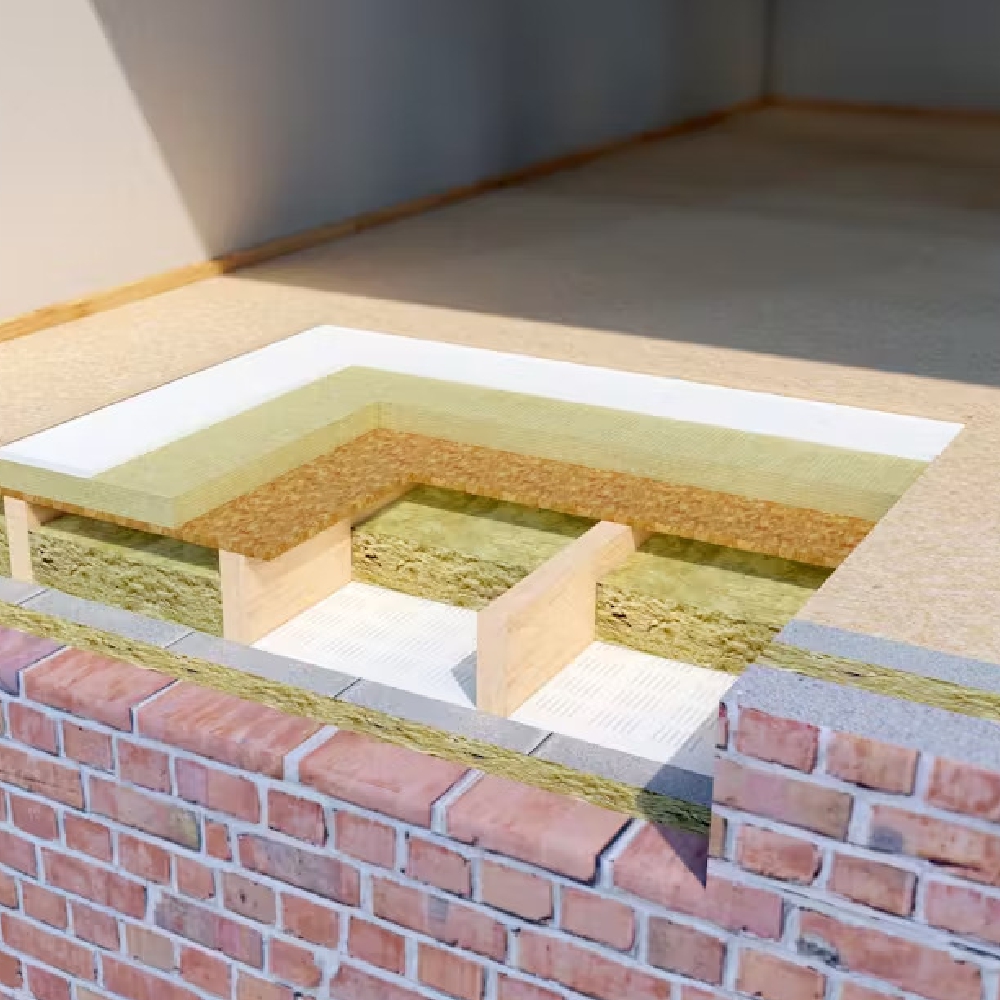
floor isulation
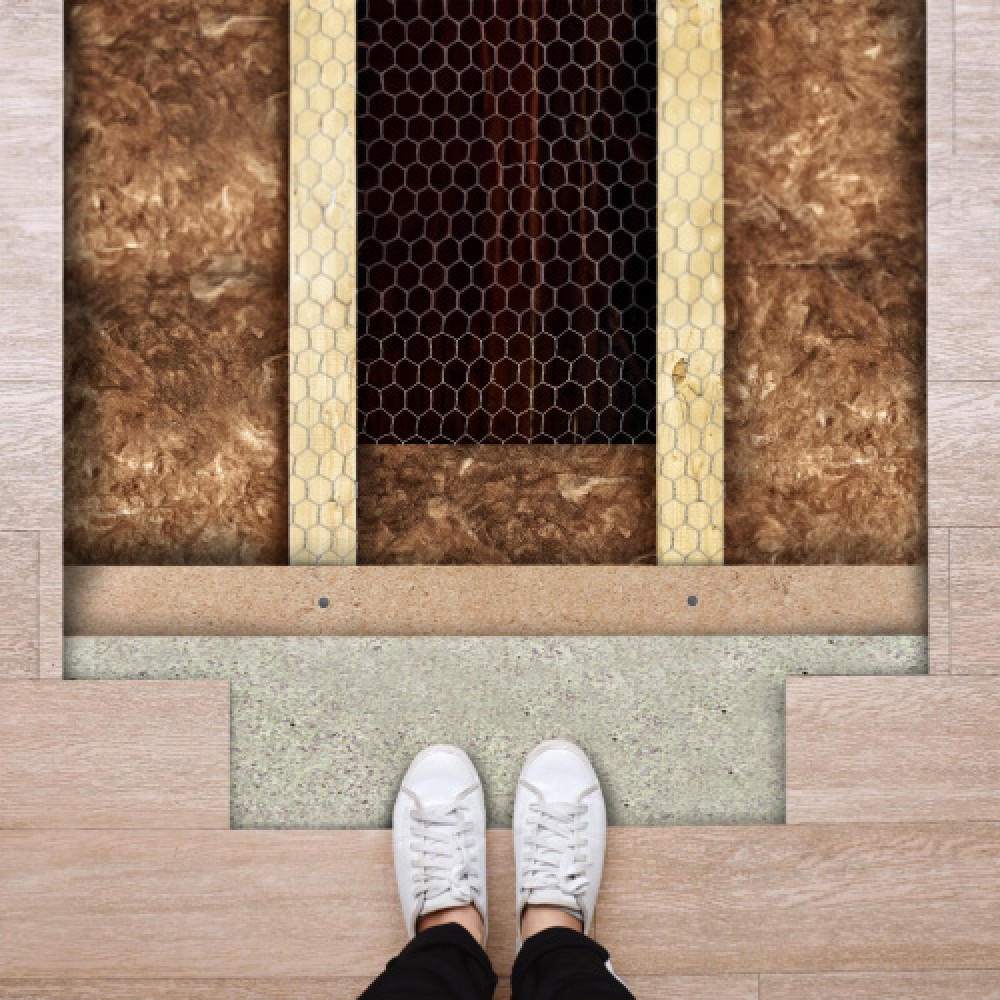
There are two main ways of insulating floor: insulating from above or insulating from below.
When insulating from above you would be able to lift any carpeting or tiling as well as the floorboards and fill between the joists with insulation material. You may wish to staple some form of netting between the joists to support the insulating material or you could nail batons to the joists so that these support the panels of insulation material that lie on top. Alternatively, rather than filling the gaps between the joists with solid insulate you could simply roll a foiled quilt, insulate across the joists, whilst pushing it down between the gaps in the joists (no more than 2 inches) and staple to the inside of each of the joists to support the quilt in place.
Insulating a floor from below is an even easier proposition (although a less likely option) which would simply pushing the insulation between the joists and using a form of mesh or netting which is connected underneath to support the insulation material in place.
*This is estimated figure based on insulating a gas-heated, semi-detached home with three bedrooms
Types of insulations
PIR - Polyisocyanurate and PUR - Polyurethane
Polyurethane (PUR) is produced by blowing a non CFC (chlorofluorocarbon) gas (usually Hydro Carbon Pentane) into urethane resin to produce a free foaming insulant (the gas used helps to improve the thermal performance of the product, but gradually escapes into the atmosphere over time). For this reason (and to stabilise the foam into boards), polyurethane and polyisocyanurate (PUR) boards are usually faced with aluminium foil. Polyisocyanurate is similar to polyurethane but usually contains long strand glass fibres within the PIR foam core which is formulated to give off less dense smoke in a fire.
PIR I PUR are mainly used as a flat roof insulation, pitched roof insulation, partial fill cavity wall insulation, domestic under-floor insulation, foamed composite panels.PIR I PUR are Suitable for temperatures up to 75°C, usually faced with aluminium foil or glass tissue.
To buy PIR insulation boards click here.
EPS - Expanded polystyrene
Polystyrene insulation is a type of rigid foam insulation which is commonly used in residential and commercial settings. It has an exceptional ability to insulate against noise and extreme temperatures. It is also waterproof and long-lasting. These qualities combine to make polystyrene insulation an exceptionally useful product.
Two types of polystyrene are used for insulation: expanded and extruded polystyrene. Expanded polystyrene, also called bead board, has a lower density that the extruded kind, and is less expensive, but also has slightly less insulating power. This is because of its coarse cells and the fact that they contain only air. Extruded polystyrene insulation has finer cells or beads, and contains a mixture of air and refrigerant gas, making it a better insulator.
XPE - Extruded polyethylene
Extruded polyethylene (XPE) is made by mixing polyethylene pellets and other ingredients, a blowing agent is injected in liquid form causing a foaming reaction. A conical shaping die is used to shape and form the XPE, producing a material that quickly cools into a flexible, closed cell plastic foam.
XPE main uses: resilient layer in acoustic floors, flexible edge strip in screeded floors.
Extruded polyethylene has excellent acoustic properties, excellent moisture resistance, good compression resistance.
XPS - Extruded polystyrene
Extruded polystyrene (XPS) is made by mixing polystyrene pellets with various ingredients to liquify them. A blowing agent is then injected into the mixture, to form gas bubbles. Next, the foaming liquid is forced through a shaping die. When cooled, it produces a closed-cell foam that is rigid and moisture resistant.
XPS is mainly used as ground floor insulation, heavy duty floor insulation and flat roofs insulation.
Extruded polystyrene is suitable for temperatures up to 75°C, it is very rigid and can be cut various component shapes and thicknesses.
Typically available in 2.4m x 1.2m or 2.4m x 0.6m sheets.
Multi layred foils
These consist of multiple sheets of aluminised polyester separated by thin sheets of polyethylene foam.
To be effective, the outer faces must face an unventilated cavity in the construction.
Multifoils are mainly used for pitched roofs in hot climates, to stop heat build-up
and it is very effective in heat retention in winter.
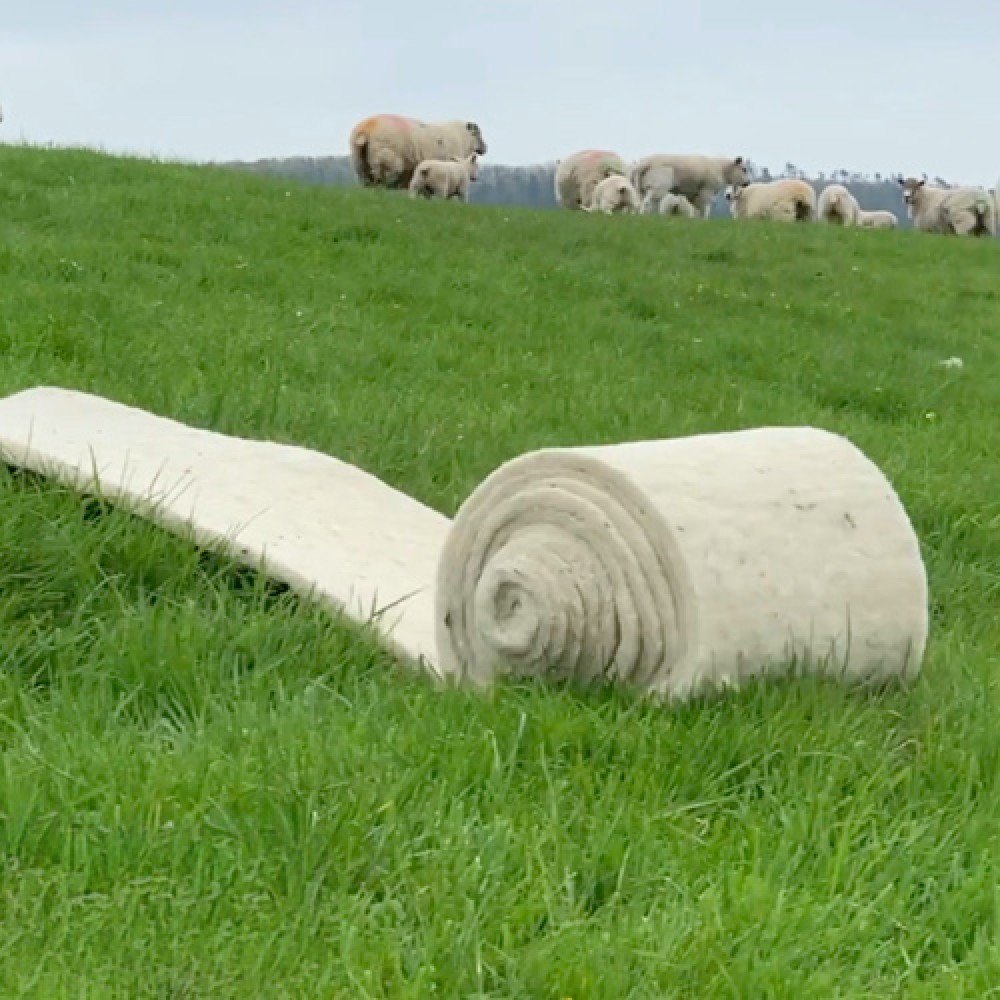
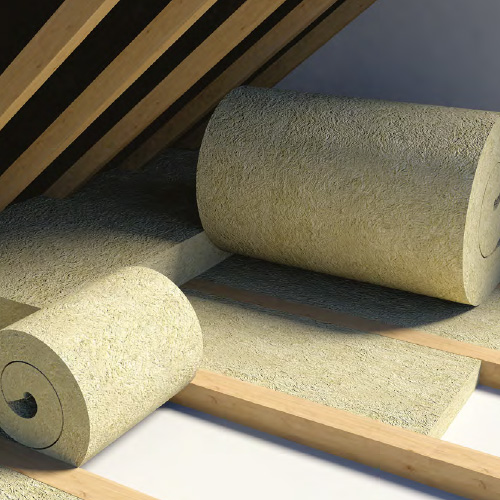
Glass mineral wool
Glass mineral wool is made from sand and recycled glass, limestone and soda ash.. The glass is spun to form millions of fine fibres.
A resin is used to bind the long fibres together to form a mat of material giving good tear strength.The density of the product determines
whether the insulation is a lightweight quilt supplied in rolls, a flexible slab or a rigid slab, and it’s thermal insulation value.
Glass wool is mainly used as a loft insulation, cavity wall insulation, sound insulation within partitions and floors.
Glass wool is suitable for temperatures up to 230°C
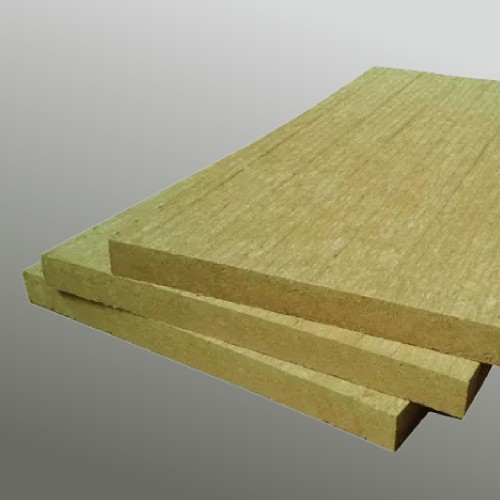
Rock Mineral wool
Rock mineral wool is made mainly from volcanic rock, typically basalt and/or dolomite. An increasing proportion is now recycled
material from slag, a waste product from blast furnaces. The materials are melted and then spun into fine fibres.
A resin is used to bind the fibres together to form a mat of insulation.
Rock mineral wool is mainly used as a thermal insulation of flat roofs, rainscreen facades and external wall insulation,
Fire protection (including smoke and fire barriers) high temperature applications, sound insulation for floors and walls.
Rock mineral wool is suitable for temperatures up to 850°C and is denser than glass mineral wool.