Floor Insulation
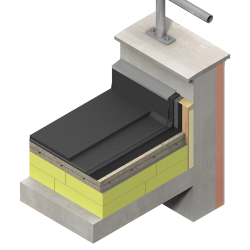
When insulating a concrete slab floor, two choices are available: insulating below or above the slab. The heating pattern should be considered before deciding which method of insulation will be used. When quick heating response time is required, for example when a family returns home in the evening, insulation above the slab should be used. Where heating is used over prolonged periods for example when the house is occupied throughout the day, the thermal mass of a slab placed above the insulation should be considered to reduce temperature fluctuation and provide steady temperatures (slower heating and cooling of space). Those considerations will allow most efficient use of heating energy.
Amount of load the insulation will be exposed to should also be considered prior to deciding which type of material is best for the insulation; to ensure adequate compression resistance of an insulation product and to lower the effects of the compressive load applied by any loading. Two types of load can be distinguished: dead load and design load.
Dead load is the weight of the floor finish upon the insulation material.
Design load is the load applied in use e.g. furniture. Point loading should be considered in calculating the required thickness of floor finish, particularly where the insulation is located above the slab.
When insulating above the concrete slab, the floor finish over the insulation can be either screed or boarding. It is argued that a screed finish is more durable and can offer some thermal mass otherwise absent. Board finishes, on the other hand, can be quickly installed and provide a quicker thermal response time.
In a timber suspended floor a range of insulation materials can be fitted between the joists to reduce overall heat loss. One of the most important issues with timber floors is their vulnerability to air leakage. Where old floorboards are relayed or new ones installed, careful attention is needed to ensure that all joints between boards are adequately sealed. Insulation should be taken right up to the edge of the floor and any space close to the outside wall filled with insulation to avoid any gaps.
To summarize, insulation above the slab increases the heating response time. Temperatures will increase more quickly when the heating system is switched on in comparison with below slab insulation. In this setting the insulation zone can be used to run services and under-floor heating. The effect of temperature regulation by thermal mass is unavailable in above the slab insulation. Point loading requires careful specification to make sure it does not damage the area of insulation beneath. It is not advisable to use above slab insulation in conjunction with timber-based flooring in wet rooms such as kitchens and bathrooms.
Below the slab insulation provides thermal mass which helps maintain steady temperatures. As a result, rooms take longer to heat in comparison with an above-slab technique. This is particularly useful in south-facing rooms. In this setting thickness of insulation is less restricted than for an above-slab condition and point loading is less of an issue because the load is spread over the concrete slab.
Suspended timber floor provides relatively quick heating response time. It also ensures minimal additional loading to the structure. This setting provides no thermal mass which causes high fluctuation of floor temperature. It can also be prone to air leakage and maintaining sub-floor ventilation can reduce the effectiveness of the insulation.
Insulationshop.co offers wide range of floor insulation products from manufacturers: KNAUF, URSA, KAY METZELER, XTRATHERM and CELOTEX suitable to use with all kinds of floor specification. For more information about particular product please see product description.
R-value Comparison Chart of Floor Insulation products available at Insulation Shop
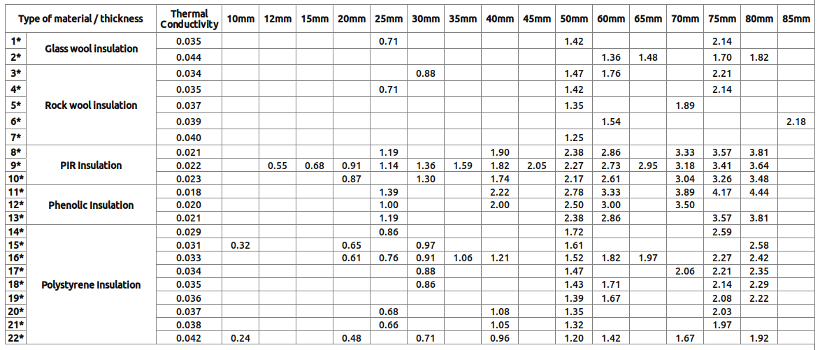
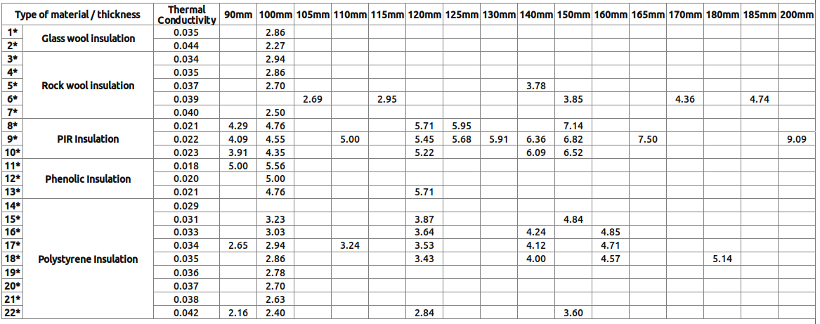
Legend
1* URSA Acoustic Insulation Roll
2* Superglass Multi Acoustic Insulation Roll
3* Rockwool RW3 Slab (Prorox SL 930)
4* Earthwool Acoustic Insulation Roll, Earthwool RS45 Universal Slab, Earthwool RS60 Universal Slab, Earthwool RS100 Universal Slab, Rockwool RWA45 (Prorox SL920)
5* Earthwool Flexible Slab, Rockwool Flexi Insulation Slab
6* Rockwool Hardrock Multi-Fix Dual Density Board
7* Rockwool RW5 Slab (Prorox SL960)
8* Celotex FI5000 Insulation Board, Celotex FR5000 Fire Resistant Insulation Board
9* Celotex TB4000 Insulation Board, Celotex GA4000 Insulation Board, Celotex XR4000 Insulation Board, Xtratherm Thin-R Insulation Board, Xtratherm Thin-R Hyfloor Insulation Board, Recticel Eurothane GP Insulation Board
10* Kingspan Thermafloor TF70 Insulation Board
11* Kingspan Kooltherm K103 Floorboard
12* Kingspan Kooltherm K3 Floorboard
13* Xtratherm Safe-R insulation Board
15* Grey Polystyrene (Graphite) EPS
16* Floormate 300A XPS, Cellecta Hexatherm XFLOOR 250 XPS, Cellecta Hexatherm XFLOOR 300 XPS, Cellecta Hexatherm XCHiP Thermal Laminate Chipboard, Cellecta Hexatherm XCPL Board, Ravatherm Polyfoam Floorboard Standard and Extra Grade
17* Cellecta Hexatherm XFLOOR 500 XPS, Cellecta Hexatherm XCHiP Thermal Laminate Chipboard, Cellecta Hexatherm XCPL Laminated Board, Sundolitt XPS300 Extruded Polystyrene Board, Ravatherm Polyfoam Floorboard - Super grade
18* Cellecta Hexatherm XPOOL Swimming Pool XPS Insulation Board, Kingspan Styrozone N300R XPS Board, Cellecta Hexatherm XFLOOR 500 Thermal Floor Insulation Board
19* EPS100 Polystyrene Insulation Board Jablite, Kingspan Styrozone N500R XPS Board