Going Green with Home Insulation
by Mark Row
 Think about the Mother Earth
Think about the Mother Earth
Environmental conciseness has grown over the years, mostly due to the fact that a large number of pollutants threatening to endanger our Mother Earth and eventually the very survival of mankind have appeared in time. This is why people are constantly trying to find alternative ways to keep a modern and industrial society but reduce its harmful environmental impact. In such process, many conflicts appeared that needed to be harmonized. One such conflict is the one between having a well insulated home and reducing the negative effect that producing and installing certain insulation materials can have to the environment. Note that there is a solution for both. Namely, you can have a well protected and insulated home without having to worry how dangerous it can be for the nature. All it takes is some basic knowledge and a bit of effort in choosing the most appropriate insulation material and you can go green with your home insulation.
To Insulate or not to Insulate?
As the environmental awareness grew, more and more processes which have never been before deemed as harmful began to be evaluated. The biggest problem with certain issues was the fact that they can go both ways, that is they can protect the Earth in one way, but also endanger it in another. So, these two effects needed to be somehow harmonized, instead of being exclusive to one another. Such typical example is insulation.
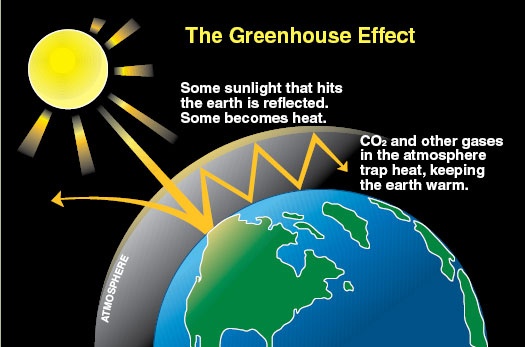
Namely, it is well known that turning your heating and cooling devices on leads to higher fuel consumption (and in the chain of events to more fuel produced) which only increases the harmful CO2 emissions into the atmosphere. You are probably starting to see the big picture now. Basic function of insulation is to limit just that. It simply improves your home thermal performance, by balancing the inner temperature – it is warmer inside when it’s cold outside and the other way around. This way there is no need to waste fuel on your cooling and heating devices again resulting in reduction of the so called carbon footprint.
On the other hand producing certain insulation materials can also have the same effect. We’ll try to break it down for you. There are two important aspects of environmental impact of insulation. The first one is the so called "embodied energy", shown through the GWP or the global warming potential. Just take the previously said on CO2 emissions and apply it here. Certain amount of fuel is used to produce insulation materials, which leads to the greenhouse gas emissions (just as in using heating and cooling devices). The other aspect is the blowing agent used in insulation product manufacturing process, such as HFC blowing agents which have very high level of potency. This other aspect is important only in the words of the agent leaking over time. However, the time needed for such process cannot be precisely determined but depends on the life of insulation. Now when these two aspects are combined, what you get is the so called lifetime GWP.
Now the only thing left to do is just estimate whether can the harmful environmental effects of insulation be nullified by its positive effects, that is to determine the “payback” of the lifetime GWP, which will always depend on the particular product in question.
Some Green Alternatives
Although everything above mentioned may sound scary, we would still not recommend that you give up on insulation, especially bearing in mind how important can it be also for your health and the commodity of everyday life. There are two ways you can fight the cold but still go green with insulation.
The first one includes using some green insulation alternatives, such as:
- Recycled denim insulation, made from parts of post-industrial denim afterwards mixed with boron in order of adding a fire protective layer and a binding agent such as polyolefin. Since it involves using industrial waste, it simply means that such waste will, instead of decomposing (which leads to greenhouse gasses emissions) be put to an alternative use. Also this lowers the transport emissions since less material is transported from the factory.
- Recycled paper cellulose insulation is another green insulation alternative. Basically, all that paper waste is put to a good use, that is transformed into cellulose-based insulation which can be, believe it or not, up to 38% more energy efficient than some alternatives like fiberglass and still have very low embodied energy.
- Bio-based spray foam insulation is another innovative solution which includes natural materials such as recycled soda cans or soy oil, either sprayed or poured into destined cavities.
- Hemp insulation is another way to go. It is made from hemp fiber and reinforcing cotton or polyester, commonly used as an alternative to fiberglass insulation. Not only that the very process of growing hemp is extremely eco-friendly (since it can be grown without the use of dangerous chemicals) but another positive thing is that the material can be recycled and reused or composted.
Finally, another way to have green home insulation is to always buy insulation products from renowned manufacturers and check the material’s package for harmful blowing agents (such as HFC) and the GWP value of the product. Bearing in mind the importance of ecology nowadays, many manufacturers have decided to use more eco-friendly solutions and are proud to show it, so don’t be surprised if you see a note on the package that the product is “HFC free” or that the GWP is 0 (or less than 5) since now you’ll know what it means. Here at Insulation Shop, we are proud to offer an additional category of our eco-products made from sheep wool as being one of the most energy efficient but also eco-friendly insulation material available today.
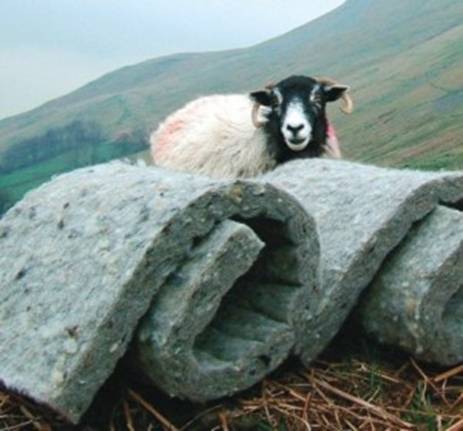

For more information about Eco-friendly Insulation Materials read the related blog articles and product descriptions on our website. If you have any questions please post them in the comments below.

















































































































